2. 成飞医院 放射科, 四川 成都 610091
2. Radiology Department, Chengfei Hospital, Chengdu 610091, Sichuan, P. R. China
2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)占糖尿病90%以上,患者多在40岁以后发病。T2DM患者体内的胰岛素相对缺乏,严重影响患者的生活质量[1, 2]。冠心病是冠状动脉血管发生动脉粥样硬化病变而引起血管腔狭窄,可造成心肌缺氧。冠心病的发生与多种因素相关,糖尿病也是主要因素之一[3, 4]。T2DM合并冠心病患者冠脉狭窄程度通常更为严重,且多支血管病变发生率高,相对于患者管腔狭窄程度,斑块稳定性对评估急性冠脉事件更有价值[5]。冠脉造影是诊断冠心病的金标准,但是随着多排双源CT的广泛应用,对诊断T2DM合并冠心病有较高的敏感性和特异性,能准确反映冠状动脉病变[6]。多排双源CT是一种无创、可靠的影像学诊断技术,本实验中应用的64排双源CT扫描最薄层可达0.64 mm,是目前世界上能达到的最薄层厚,从而提高了图像的分辨率,因此人们对应用64排双源CT研究冠脉狭窄程度及斑块稳定性寄予很高的期望[7, 8]。本研究旨在探讨64排双源CT对T2DM合并冠心病患者冠脉狭窄程度及对斑块稳定性的诊断价值。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料选择2015年2月~2018年2月我院接诊的90例冠心病患者做为本次研究对象,分为两组:合并T2DM为观察组:男28例,女21例,年龄57~74岁,平均(63.54±3.52)岁;未合并T2DM为对照组:男24例,女17例,年龄58~74岁,平均(63.58±3.61)岁。两组一般资料见表 1。纳入标准:(1)符合《冠心病诊断与治疗研究进展》诊断标准[9];(2)无严重肝肾功能障碍者;(3)患者知情同意并签署相关知情同意书。排除标准:(1)患有意识障碍、精神障碍者;(2)伴有恶性肿瘤患者;(3)恶性血液病患者。
| 表 1 两组患者一般资料比较 |
使用德国西门子公司所生产的SOMATOM Definition Flash双源CT机,应用心电门控技术,患者保持仰卧位,一次性屏住呼吸,进行CT平扫,扫描参数:管电压120 kV,管电流650 mA,准直器宽0.625 mm×64,螺距0.16:1,显示野250 mm,矩阵512×512。扫描范围自气管隆突下2 cm至膈下2 cm。先经头静脉团注20 mL欧乃派克(350 mg/mL, GE healthcare),流率4.0 mL/s,进行预扫描,测主动脉根部增强峰值时间,将此时间加上10s作为冠状动脉CT扫描的延迟时间。然后按确定扫描范围行增强扫描,经头静脉以4.0 mL/s流率注射欧乃派克50 mL,再注射20 mL 0.9%氯化钠溶液,流率为4.0 mL/s。所有患者心率控制在70次/分以下,按确定的延迟时间扫描。根据CT值结合其密度把冠状动脉斑块分为:①软斑块:CT值小于60 HU且密度比增强的冠状动脉管腔低,无任何钙化影;②钙化斑块:CT值大于120 HU且斑块以高密度成分为主;③混合斑块:CT值介于60 HU与120 HU之间且斑块中混有钙化影。
1.3 统计学分析数据用SPSS 18.0软件包进行处理,计量资料均用(x±s)表示,采用t检验;计数资料以[n(%)]表示,采用χ2检验。以选择性冠状动脉造影为金标准,计算出64排双源CT检查的敏感性、特异性、准确性以及阳性预测值和阴性预测值。P < 0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 两组患者用64排双源CT发现斑块的性质比较观察组发现的软斑块和混合斑块均显著多于对照组,钙化斑块则少于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 2。
| 表 2 两组64排双源CT斑块性质比较[n(%)] |
两组患者冠状动脉Ⅰ级、Ⅱ级、Ⅳ级狭窄无明显差异(P>0.05);观察组Ⅲ级狭窄显著多于对照组(P < 0.05),见表 3。
| 表 3 两组冠状动脉狭窄程度CT显示结果比较[n(%)] |
64排双源CT对≥50%冠状动脉狭窄诊断的灵敏度最低,随着病变的加重,灵敏度逐渐上升。阳性预测值随病变增加而增加,但都较阴性预测值为低,表明64排双源CT评价冠状动脉病变时存在高估现象;冠状动脉钙化较为严重,不同钙化程度对诊断的影响总体表现为随钙化程度变严重,其诊断特异性下降,但仍可保持较高的灵敏度和准确率,见表 4、表 5和图 1。
| 表 4 64排双源CT对中、重度狭窄冠状动脉的评价结果 |
| 表 5 64排双源CT对不同钙化程度冠状动脉的评价结果 |
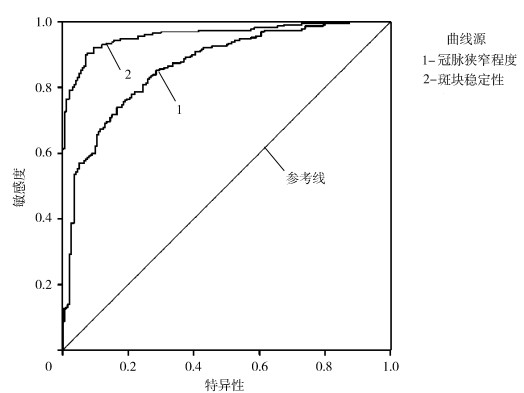
|
图 1 64排双源CT诊断T2DM合并冠心病患者冠脉狭窄程度及斑块稳定性的ROC曲线 |
冠心病和DM都是威胁人类健康的主要疾病,冠心病是以冠状动脉粥样硬化为病理变化的心血管疾病,糖尿病性血管病变表现为动脉壁中层钙化引起的管腔狭窄,T2DM冠心病发病率远大于非糖尿病患者[10]。有研究显示,T2DM患者除高血压、吸烟等冠心病危险因素外,还具有如高胰岛素血症、高氧化应激状态等,都可引起动脉粥样硬化的发生[11]。冠状动脉粥样硬化是累及体循环系统的动脉内膜疾病,斑块破裂是其常见的并发症,占心肌梗死或冠状动脉猝死的70%,故对斑块稳定性的研究较为重要[12]。64排双源CT为不稳定斑块的无创性检查提供了新的途径,不仅能够检测冠状动脉粥样硬化斑块,还能探测冠状动脉狭窄程度,同时具有较短的旋转时间和高时间分辨率,可确认脂肪、水、纤维成分,且还有较高的敏感性与特异性[13]。侯新民等[14]研究报道显示,64排双源CT用于检测冠状动脉粥样硬化斑块能显示斑块的特性,反映斑块间密度的差异。
相关研究认为,动脉粥样硬化斑块的形成非常复杂,可根据影像和CT结果分为软斑块、混合斑块及钙化斑块,非钙化斑块即软斑块和混合斑块属于不稳定斑块,容易引起不稳定型心绞痛,易于破裂,当发生破裂时可形成血栓,引发冠状动脉急性突发事件,而钙化的斑块虽可导致管腔局部负性重构的发生,但较为稳定[15-17]。本研究将64排双源CT应用于动脉粥样硬化患者中,研究结果显示,T2DM合并冠心病患者软斑块、混合斑块及钙化斑块均显著多于单纯冠心病患者,说明T2DM合并冠心病患者斑块更容易破裂出血,故心血管事件发生的风险更高。且T2DM合并冠心病患者Ⅲ级狭窄显著多于单纯冠心病患者。国外研究结果也显示,64排双源CT冠状动脉成像能准确检出非钙化斑块和混合斑块等不稳定斑块,为临床治疗、预防猝死提供重要价值[18]。64排双源CT具有较短的旋转时间、高空间分辨率和高时间分辨率,其敏感性和特异性高达99%和95%。王平等[19]研究显示,64排双源CT能够准确评价T2DM合并冠心病患者冠脉狭窄程度。本研究结果显示,64排双源CT对T2DM患者冠状动脉病变的诊断敏感性为92.54%, 特异性为93.58%,阳性预测值为82.97%,阴性预测值为97.39%,准确率为93.36%,对重度以上患者的诊断价值优于中度病变患者,与卢伟光等[20]的研究结果相似。64排双源CT在诊断T2DM合并冠心病时能够准确地显现出冠状动脉病变的情况,其对同钙化程度的冠状动脉都具有较高的敏感性。国外研究显示,随着钙化积分的增高,64排双源CT判断狭窄程度在50%以上的冠脉病变的特异性在下降,但仍具有较高的预测值,且敏感性也保持在97%以上[21]。本研究结果显示,64排双源CT评估冠脉钙化病变具有较高的敏感性和特异性,虽然随钙化程度增高,其特异性也在下降,但也可达到87.39%,且保持了较好的敏感性和阳性预测值。上述结果说明64排双源CT具有较高的阴性诊断可靠性,能够对T2DM合并冠心病做出准确的评估。这可能是因为64排双源CT作为新型的CT技术,采用了滑环技术,使其能够进行17节段评估,故敏感性与特异性较高。
综上所述,多排双源CT对T2DM合并冠心病患者冠脉狭窄程度及斑块稳定性的诊断价值较高,可帮助临床提供正确诊断,以选择合适的治疗方案。
| [1] |
刘金刚, 郑成竹, 王勇. 中国肥胖和2型糖尿病外科治疗指南(2014)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2014, 8(11): 1005-1010. Liu J G, Zheng C Z, Wang Y. Guidelines for the surgical treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes in China (2014)[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery, 2014, 8(11): 1005-1010. |
| [2] |
母义明, 陈康. 成人2型糖尿病胰岛素临床应用中国专家共识解读[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2012, 29(3): 1-6. Mu Y M, Chen K. Interpretation of Chinese expert consensus on clinical application of insulin in adult type 2 diabetes[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Frontier (Electronic Edition), 2012, 29(3): 1-6. |
| [3] |
Wu J, Xun P, Tang Q, et al. Circulating magnesium levels and incidence of coronary heart diseases, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. Nutrition Journal, 2017, 16(1): 60. |
| [4] |
Levelt E, Piechnik S K, Liu A, et al. Adenosine stress CMR T1-mapping detects early microvascular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus without obstructive coronary artery disease[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 19(1): 81. |
| [5] |
刘虹宏, 张京梅, 李志忠, 等. 经皮冠状动脉介入术后大剂量阿托伐他汀对冠状动脉多支病变合并2型糖尿病患者黏附分子和炎性指标及颈动脉斑块面积的影响[J]. 中国医药, 2017, 12(11): 1609-1613. Liu H H, Zhang J M, Li Z Z, et al. Effects of high-dose atorvastatin on adhesion molecules and inflammatory indicators and carotid plaque area in patients with coronary multi-branch disease complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus after percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Chinese Medicine, 2017, 12(11): 1609-1613. |
| [6] |
陈梅桂, 赖清泉, 魏丽珍, 等. 双源CT评价糖尿病合并高血压患者左心功能的临床应用价值[J]. 糖尿病新世界, 2019, 22(9): 13-16. Chen M G, Lai Q Q, Wei L Z, et al. Clinical application value of dual source CT in evaluating left ventricular function in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension[J]. New World of Diabetes, 2019, 22(9): 13-16. |
| [7] |
李建华, 王璟, 王磊, 等. 双源CT冠状动脉成像结合胸痛表现在冠心病诊断中的应用[J]. 安徽医药, 2019, 23(4): 651-653. Li J H, Wang J, Wang L, et al. Application of dual source CT coronary angiography combined with chest pain in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease[J]. Anhui Medicine, 2019, 23(4): 651-653. |
| [8] |
徐佳欢, 张文雯, 吕宇航, 等. 第3代双源CT低剂量Turbo Flash成像图像质量与诊断效能的临床研究[J]. 国际放射医学核医学杂志, 2018, 42(6): 500. Xu J H, Zhang W W, LV Y H, et al. Clinical study on image quality and diagnostic efficiency of the third generation dual source CT low dose turbo flash imaging[J]. International Journal of Radiation Medicine and Nuclear Medicine, 2018, 42(6): 500. |
| [9] |
胡大一. 冠心病诊断与治疗研究进展[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2003, 31(11): 806-811. Hu D Y. Research progress in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Disease, 2003, 31(11): 806-811. |
| [10] |
周欢, 周红微, 戴婉如. 糖化血清白蛋白与2型糖尿病并发冠心病的相关性研究[J]. 实验与检验医学, 2019, 37(3): 492-495. Zhou H, Zhou H W, Dai W R. Correlation between glycosylated serum albumin and coronary heart disease in type 2 diabetes[J]. Experimental and Laboratory Medicine, 2019, 37(3): 492-495. |
| [11] |
Stratmann B, Richter K, Wang R, et al. Metabolomic signature of coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2017, 3(1): 1-9. |
| [12] |
Madhu S V, Aslam M, Aiman A J, et al. Prevalence of hypogonadism in male type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with and without coronary artery disease[J]. Indian Journal of Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2017, 21(1): 31-37. |
| [13] |
任燕, 吴军, 钱伟伟, 等. 炫速双源CT心周脂肪及心外膜脂肪体积测定与冠状动脉粥样硬化的相关性研究[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2018, 2(2): 168-169. Ren Y, Wu J, Qian W W, et al. Study on the correlation between measurement of pericardial fat and epicardial fat volume and coronary atherosclerosis with dual source CT[J]. Imaging Research and Medical Application, 2018, 2(2): 168-169. |
| [14] |
侯新民, 胡俊, 陈彩美. 64排螺旋CT与选择性冠脉造影评价急性冠脉综合征患者易损斑块特征分析[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2017, 21(24): 61. Hou X M, Hu J, Chen C M. 64 slice spiral CT and selective coronary angiography in the evaluation of vulnerable plaque characteristics in patients with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Journal of Practical Clinical Medicine, 2017, 21(24): 61. |
| [15] |
Dale C, Fatemifar G, Palmer T, et al. Causal associations of adiposity and body fat distribution with coronary heart disease, stroke subtypes and type 2 diabetes: a mendelian randomization analysis[J]. Circulation, 2017, 135(24): 2373. |
| [16] |
Agarwal G, Singh S K. An intriguing family with type 2 diabetes mellitus and complete heart block[J]. Indian Journal of Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2017, 21(5): 784-786. |
| [17] |
Mani D, Chinniah R, Ravi P, et al. Predisposition of angiotensin-converting enzyme deletion/deletion genotype to coronary artery disease with type 2 diabetes mellitus in south india[J]. Indian Journal of Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2017, 21(6): 882-885. |
| [18] |
Bucher A M, Albrecht M H, Scholtz J E, et al. High-pitch dual-source CT angiography before TAVI - the value of ECG gating[J]. Current Medical Imaging Reviews, 2019, 15(4): 373-379. |
| [19] |
王平, 毛治尉, 白华东. 64层螺旋CT评估冠状动脉斑块的位置分布、性质及稳定性的应用价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2019, 17(2): 122-125, 157. Wang P, Mao Z W, Bai H D. The application value of 64 slice spiral CT in assessing the location, distribution, nature and stability of coronary plaque[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2019, 17(2): 122-125, 157. |
| [20] |
卢伟光, 曾怡群, 赖焕泉, 等. 64排CT诊断冠状动脉易损斑块的临床价值及危险因素分析[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2017, 15(6): 37-40. Lu W G, Zeng Y Q, Lai H Q, et al. Analysis of clinical value and risk factors of 64 slice CT in the diagnosis of vulnerable plaque of coronary artery[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2017, 15(6): 37-40. |
| [21] |
Mannil M, Hickethier T, von Spiczak J, et al. Photon-counting CT: high-resolution imaging of coronary stents[J]. Investigative Radiology, 2018, 53(3): 143-149. |



